Distal Radius Fracture
Hand & Wrist Diseases & Conditions
The forearm consists of two bones: the ulna (on the pinky finger side) and the radius (on the thumb side). The distal radius is the area of the radius that is connected to the wrist joint. A distal radius fracture is the most common arm fracture and occurs when the radius is fractured approximately one inch from the wrist.
This fracture is experienced by individuals of all ages. For young people, high-force accidents, such as car accidents and falling from moderate heights, lead to distal radius fractures. Contrastingly, older individuals or people with osteoporosis are at a greater risk of these fractures and may experience one from a simple fall.
Everyday tasks become difficult with a distal radius fracture, as the wrist often becomes near impossible to move, and finger movement is often limited.
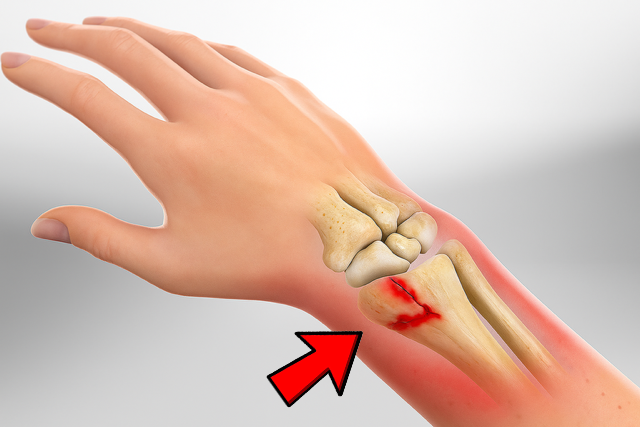
Causes of Distal Radius Fractures
There are various causes of distal radius fractures, depending on age, medical conditions and lifestyle choices. These include:
- Falling on an outstretched arm: younger individuals will require a more forceful fall than older individuals for the radius bone to fracture. Falling from a standing position causes many distal radius fractures in individuals over 60.
- Other trauma-inducing injuries: car accidents and other high-force accidents can cause these bone fractures.
- Osteoporosis and juvenile osteoporosis: these conditions can promote distal radius fractures as the radius bone is weakened, making it more susceptible to fracture.
Symptoms
Symptoms of distal radius fractures include:
- Pain and tenderness
- Swelling and bruising
- Abnormal hanging or bend of the wrist
- Unable to execute gripping or squeezing motions
- Numbness or tingling of fingers in severe cases
Types of Distal Radius Fractures
There are two main types of distal radius fractures, which are defined by the angle in which the bone breaks.
Colles Fractures
A Colles fracture is the most common distal radius fracture and occurs when the broken bone is angled upwards in the direction of the back of the hand. This primarily occurs due to impact through the palm, for example, falling on - or catching a fall with - the palms. A bump in the wrist is often visible.
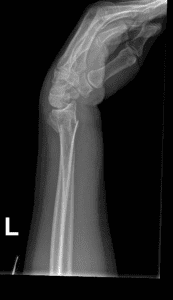
Smith Fractures
A Smith fracture is angled in the opposite direction, downwards towards the palm. This happens due to impact on the wrist's back. Such injuries are uncommon but can be caused by falling on or impacting a bent wrist.
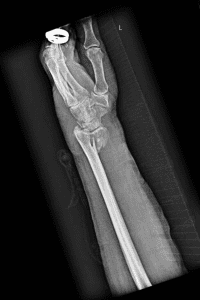
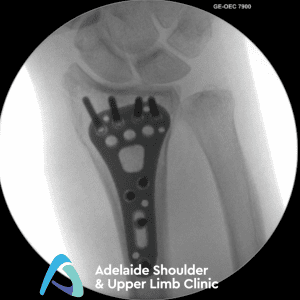
Treatments - Distal Radius Fracture Repair
Non-Surgical Treatments
There are many treatment options for distal radius fractures, depending on severity. Non-surgical treatment options include:
- The application of a cast for a healing period (usually around six weeks).
- Re-aligning out-of-place bone fragments through pushing and pulling (closed reduction with local anaesthesia) and then wearing a splint or cast.
- Monitoring via regular X-rays.
- Physical therapy (after wearing a cast or splint).
Surgical Treatments
For more severe fractures, surgery may be required for adequate healing. Fractures that often require surgery include:
- Cases where bone fragments are misaligned and cannot be corrected by closed reduction.
- When patients are experiencing numbness or tingling of fingers.
- Open breaks, where the radius bone breaks the skin.
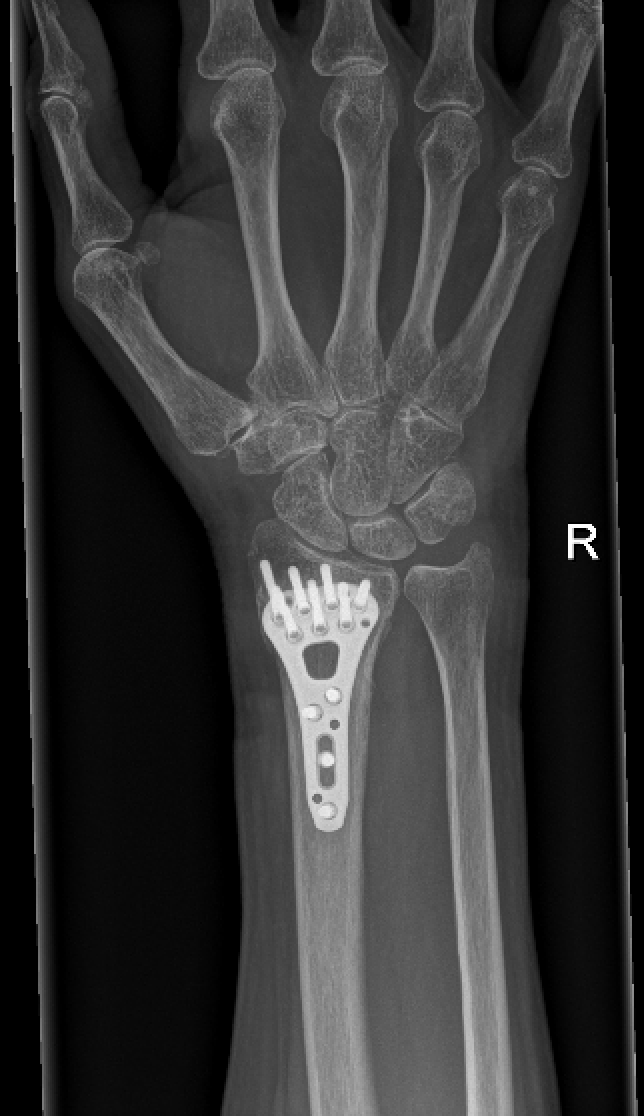
Simple Fixation
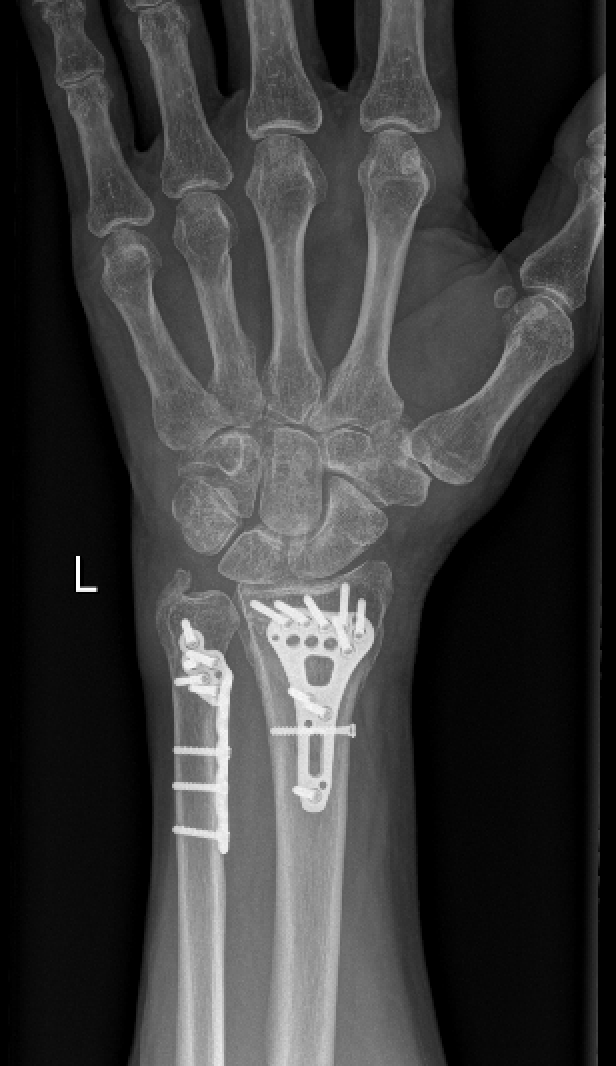
Radius and Ulna Fixation
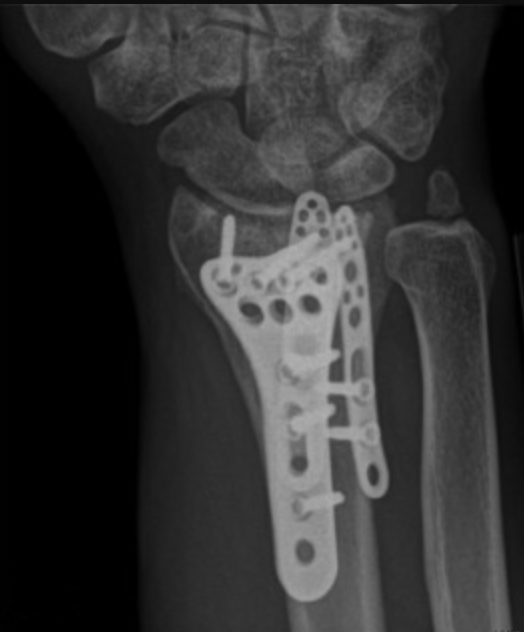
Complex Radius Fixation
Surgery on misaligned distal radius fractures involves accessing the broken radius via an incision on the wrist. Dr Oscar Brumby-Rendell, a highly qualified Orthopaedic surgeon, conducts this surgery precisely, ensuring that tendons, arteries and nerves are protected. Dr Oscar Brumby-Rendell then performs an open reduction, realigning the fragments of broken radius bone.
If an individual is experiencing numb or tingling fingers after injuring their radius bone, the hand nerves may be damaged. To avoid permanent nerve damage, surgery is often conducted to realign the bone, and healing is monitored.
For open fractures where the radius bone breaks the skin, surgery must be conducted quickly, provided that the soft tissues are not severely damaged. Here, Dr Oscar Brumby-Rendell will clean the bone and soft tissue and conduct internal fixation. During this surgery, screws or plates are implemented to align the radius fragments.
Post-Operative Care After Distal Radius Fracture Surgery
Recovery after distal radius fracture surgery is just as important as the operation itself. At our Adelaide-based upper limb clinic, we follow a structured post-operative care plan designed to promote healing, minimise stiffness, and restore wrist function. Within the first few days after surgery, patients are fitted with a custom-made thermoplastic wrist splint. This splint is specifically moulded to each individual’s anatomy, ensuring a comfortable and secure fit. Its adjustable velcro straps accommodate changes in swelling during the early recovery phase, making it far superior to generic casting.
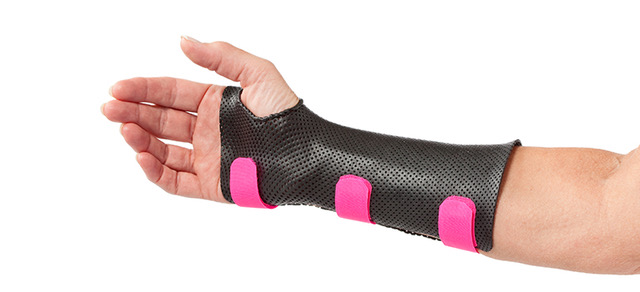
Patients typically wear the custom wrist splint for up to six weeks. However, one of the major advantages of our approach is that gentle range-of-motion exercises begin immediately, allowing early mobilisation of the fingers, elbow, and shoulder while the wrist remains protected. This early movement is critical for maintaining joint flexibility and preventing long-term stiffness — common concerns following wrist fracture surgery.
It’s also important to note that driving is generally not recommended during this recovery period, as most car insurance policies do not cover drivers who are dependent on a splint or unable to fully control the vehicle. We advise patients to plan for alternative transport during this six-week period while healing progresses.
Our goal is to provide a smooth recovery experience with a tailored rehabilitation plan. If you've sustained a distal radius fracture or broken wrist and are considering surgery, our team of experienced upper limb surgeons in Adelaide offers personalised care and proven outcomes using the latest techniques and recovery protocols.
Want to learn more?
Here are two more videos that delves deeper about Wrist Fractures and a Comprehensive Examination for both Hand and Wrist.
Once you have a referral…
Book your consultation here.